- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
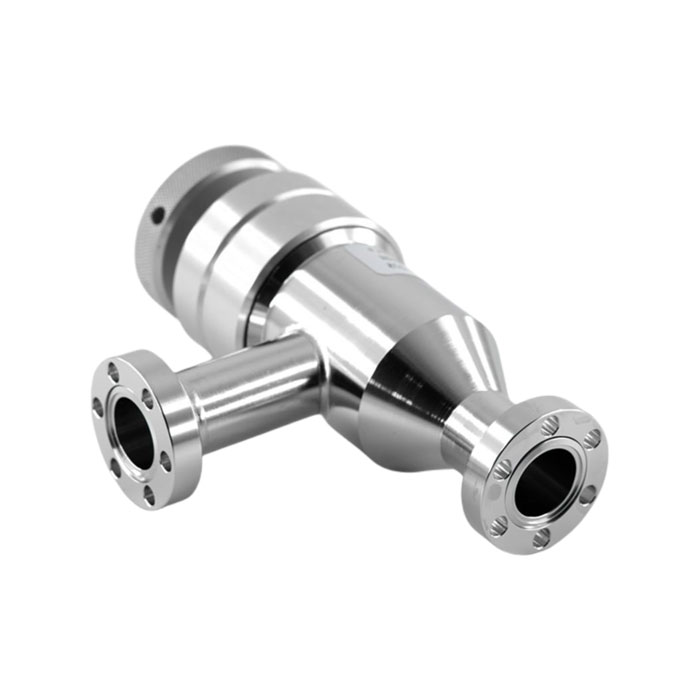
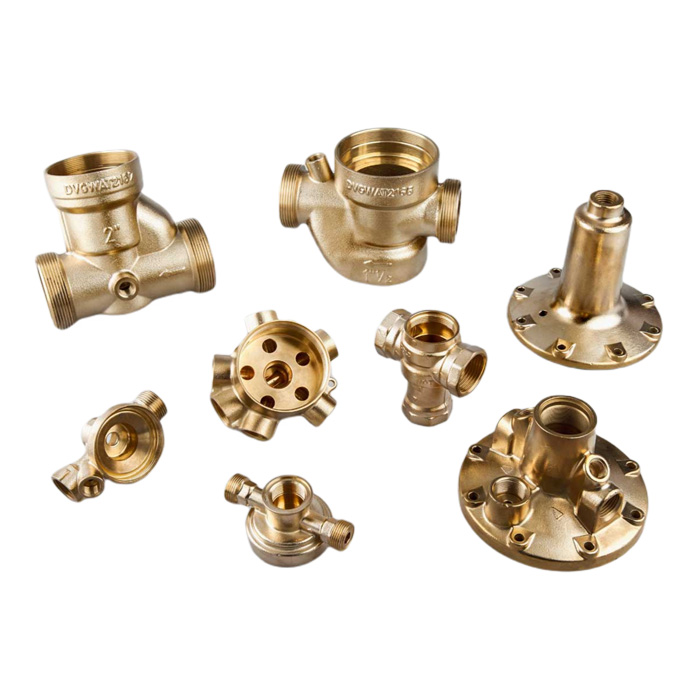
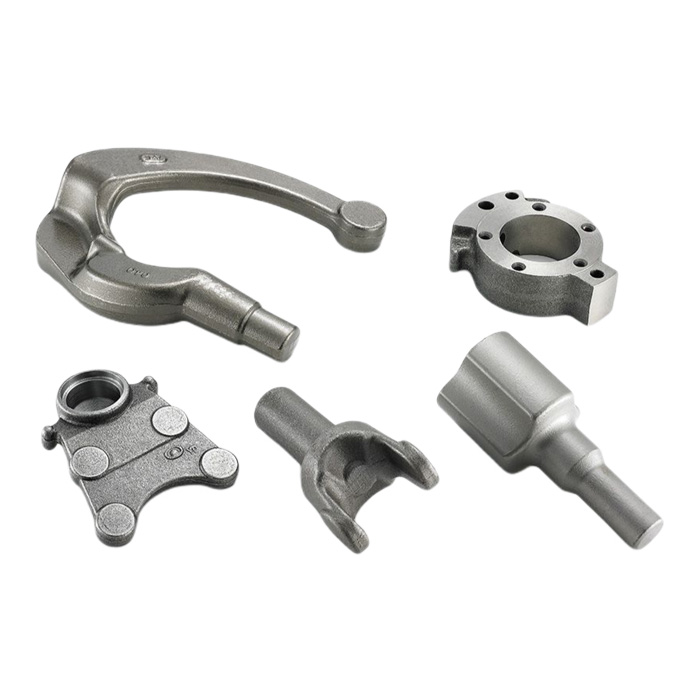
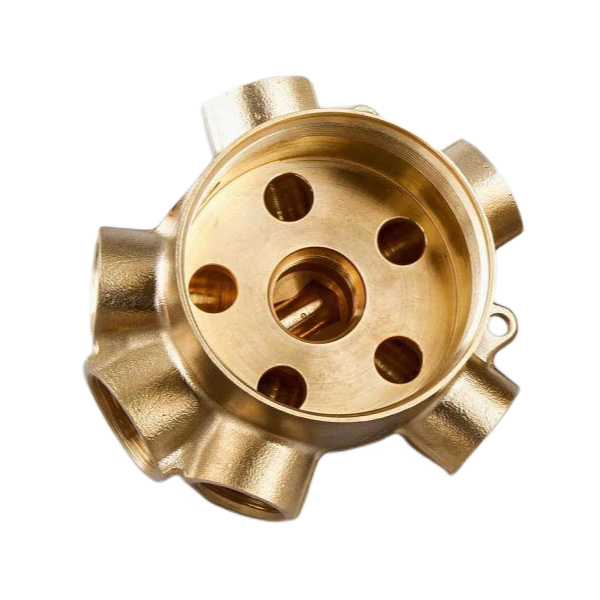
Hot Forging
Youlin® Hot forging is known to produce some of the strongest manufactured parts and components compared to other metal manufacturing processes. We produce hot forging parts and components from a few grams to more than a few hundred kilograms. For hot forging parts with special surface finish requirements, we provide a broad range of secondary operation including machining, surface finishing, etc.
Send Inquiry
Our commission is to serve our users and clients with best quality and competitive portable digital products for Special Price for China OEM Factory Manufacture Youlin® Hot Forging for Multi-Field, We are also constantly looking to establish relationship with new suppliers to provide innovative and smart solution to our valued customers.
Special Price for China Forging, Hardware, Qualified R&D engineer are going to be there for your consultation service and we are going to try our best to meet your requirements. So be sure to feel free to contact us for inquiries. You'll be able to send us emails or call us for small business. Also you are able to come to our business by yourself to get further knowing of us. And we are going to surely supply you with the best quotation and after-sale service. We're ready to build stable and friendly relations with our merchants. To achieve mutual success, we'll make our best efforts to build a solid co-operation and transparent communication work with our companions. Above all, we're here to welcome your inquiries for any of our items and service.
1.What Is Hot Forging?
Youlin® Hot forging entails the heating of a workpiece to about 75% of its melting temperature. This allows for the flow stress and energy required to form the metal to lower, effectively increasing the rate of production (or strain rate). Hot forging aids in making the metal easier to shape as well as less likely to fracture.
 Iron, along with its alloys, are almost always hot forged for two main reasons:
Iron, along with its alloys, are almost always hot forged for two main reasons:
#1) If work hardening progresses, hard materials (such as steel and iron) will become more difficult to work with
#2) It is a more economical option to hot forge metals such as steel and then follow with heat treatment processes as metals such as steel can be strengthened through other processes (and not necessarily just cold working processes).
Average temperatures for hot forging includes:
Aluminum (Al) Alloys – 360° (680°F) to 520°C (968°F);
Copper (Cu) Alloys – 700°C (1 292°F) – 800°C (1 472°F);
Steel – up to 1 150°C (2 102°F)
2.The Benefits and Unfavorable Side Effects of Hot Forging
The hot forging process produces the most various shapes compared to other forging processes, and as the dies are not very expensive to produce, it is very well adapted to small batches and shapely components.
 ✔ Good ductility
✔ Good ductility
✔ Possibility to manufacture customized parts with complex shapes
✔ High precision, excellent surface quality
✔ High formability ratios, cost benefit
✔ Enhanced stiffness and thus less energy required
✔ Increased diffusion and thus reduced chemical inhomogeneity
However, Hot Forging Features 2 Unfavorable Side Effects
✘ The functional areas of the component should be machined before assembly, as surface conditions, dimensional tolerances and residual surface contamination are not suitable to usual mechanical assembly design.
✘ The material yield is higher than other (warm and cold forging) because of the scale produced during the heating, and because of the subsequent machining.
3.The Most Important Things to Consider When Performing Hot Forging
Cooling: Cooling should be performed with an extreme care due to the risk of warpage.
Tolerances: Another important thing to consider when choosing hot forging is the less precise dimensional tolerance compared to cold forging.
Flash: Hot forgings can be divided into forgings with and without flash. These with flash possess complex 3D geometries compared to the flashless ones, generally limited to axisymmetric components or components with cyclic-symmetric geometries.
Dies: The dies used in hot forging are custom-made to match the customer’s part designs. The process is performed with drop, power drop or counterblow hammers, hydraulic or screw presses, and other similar machinery to compress the heated metal into the desired part shape. Since the dies used in hot forging undergo sever thermal cycle and mechanical loading, cracking, plastic deformation, thermal fatigue cracking and wear should be taken into account. To prolong dies’ life a good ductility and toughness and enhanced levels of both hot hardness and hot tensile strength are required.

4.Materials for Hot Forging and Application
|
Material |
Characteristics |
Application |
|
Stainless Steel |
Corrosion-resistant |
▶ Used in steam turbines, pressure vessels, and other applications in petrochemical, medical, food processing industries. ▶ Used at temperatures up to 1800 F under low stress and to 1250 F under high-stress. |
|
Low Carbon and Alloy Steel |
Easily processed Good mechanical properties Low material cost |
▶ Mainly used at temperature lower than 400 F for structural and engine applications in the aircraft and transportation industries. |
|
Aluminum |
Good strength-to-weight ratio Readily forged |
▶ Mainly used at temperature lower than 400 F for structural and engine applications in the aircraft and transportation industries. |
|
Brass |
Oxidation resistance Creep-rupture strength |
▶ Used at temperature between 1200 and 1800 F. ▶ Used for structural shapes, turbine components, fittings, and valves. |
|
Titanium |
High strength Low density Excellent corrosion resistance |
▶ About 40% lighter in weight compared to steel parts. ▶ Used primarily in the temperature services to 1000 F. ▶ Used for aircraft engine components and structures, ship components, and valves and fitting in transportation and chemical industries. |
5. FAQ
Q: What can we offer for secondary operations and heat treatment of hot forging?
A: ☆ High precision machining
★ Punching, drilling, tapping, bending, milling
☆ Painting, anodizing, black oxide, powder coating
★ Heat treatment
Q: Which industries can mostly benefit from hot forging?
A: The most common hot forged product applications are mainly found in automotive, agricultural, aerospace and construction configurations, which require strength and durability.
Q: Which is better cold forging or hot forging?
A: Cold forging improves the strength of the metal by hardening it at room temperature. Hot forging results in optimal yield strength, low hardness, and high ductility by hardening the metal at extremely high temperatures.