- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
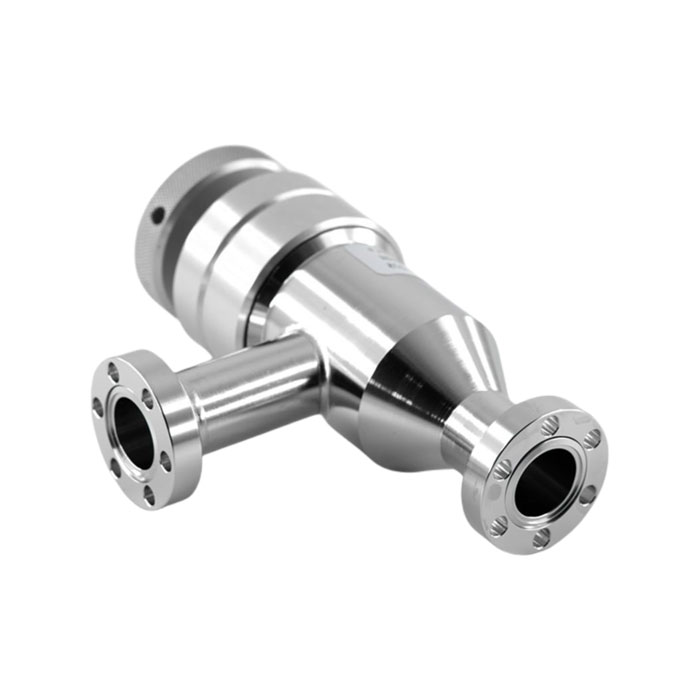
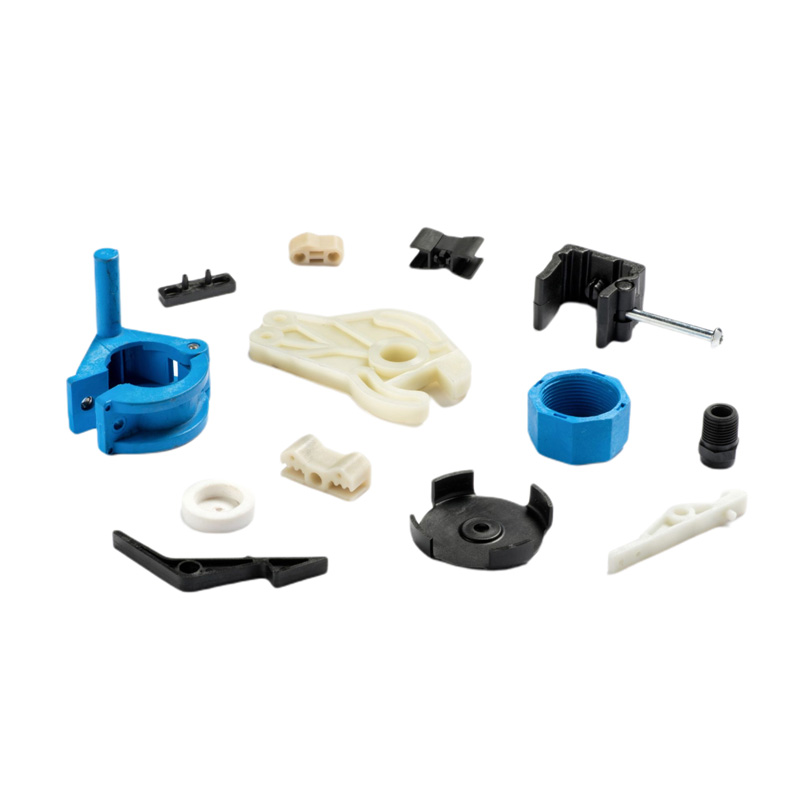
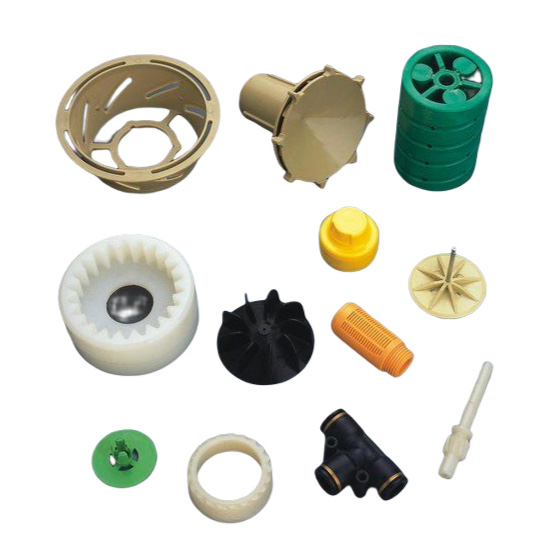
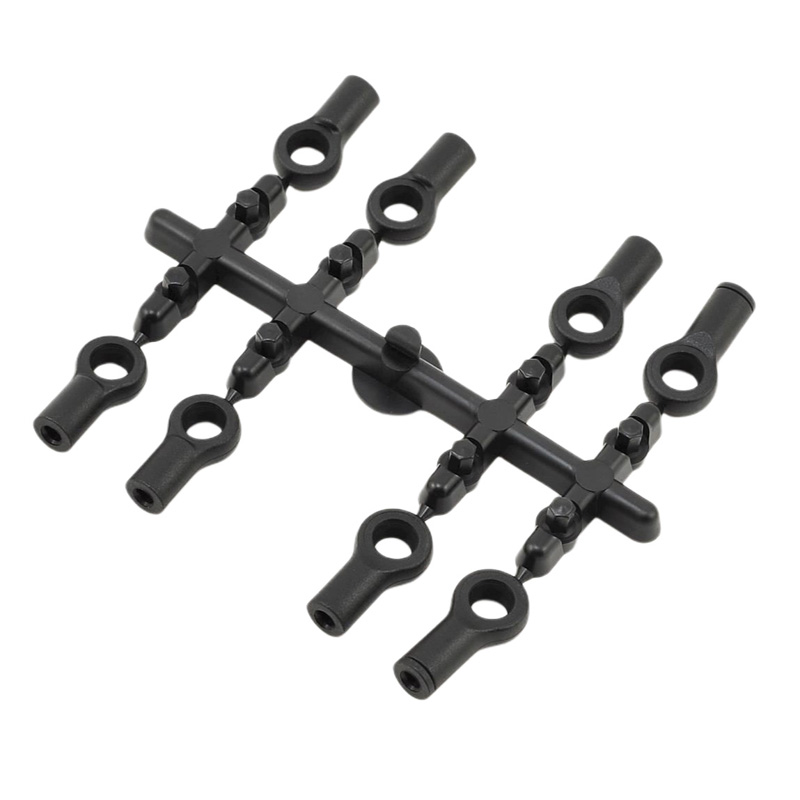
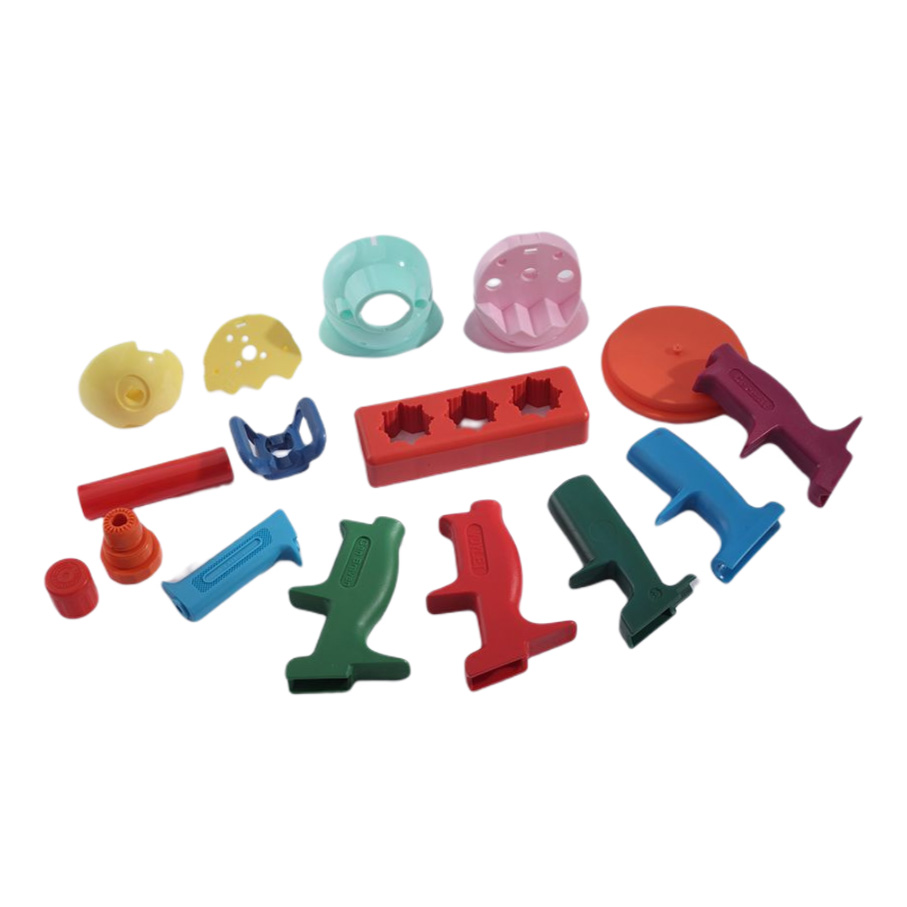
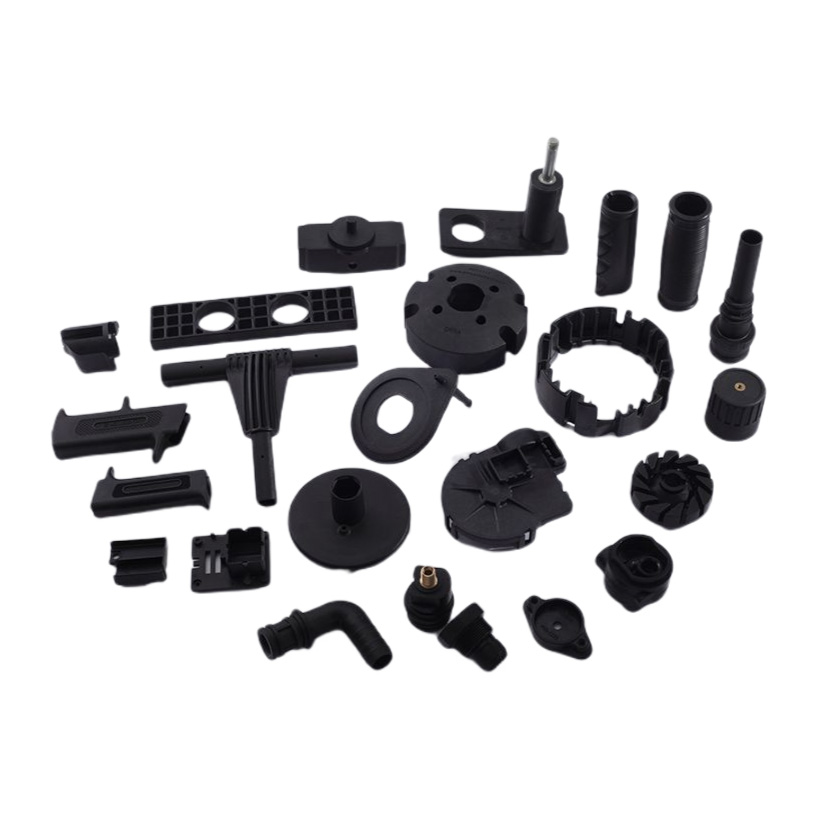
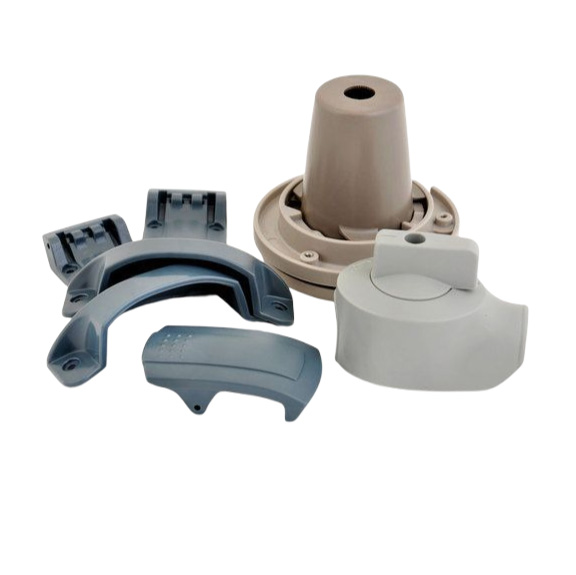
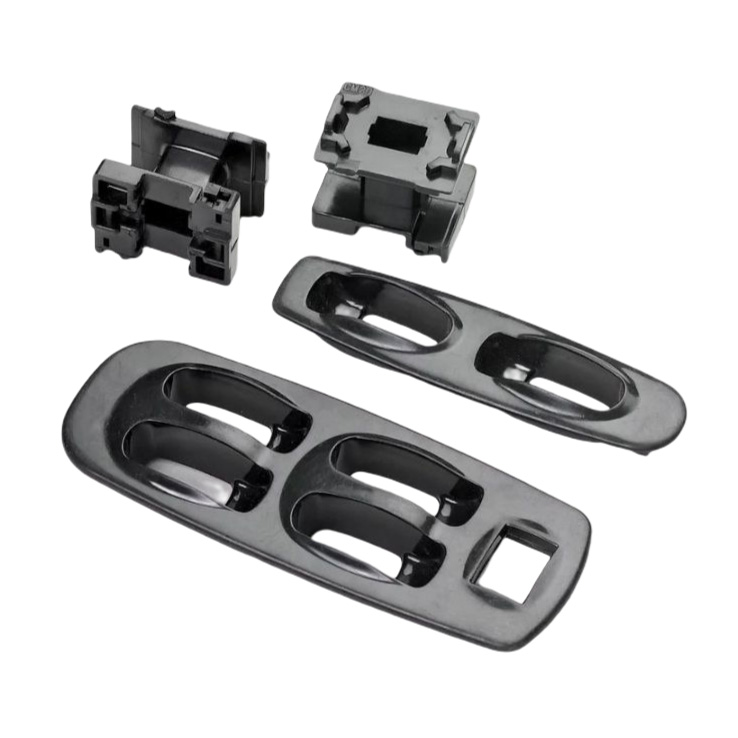
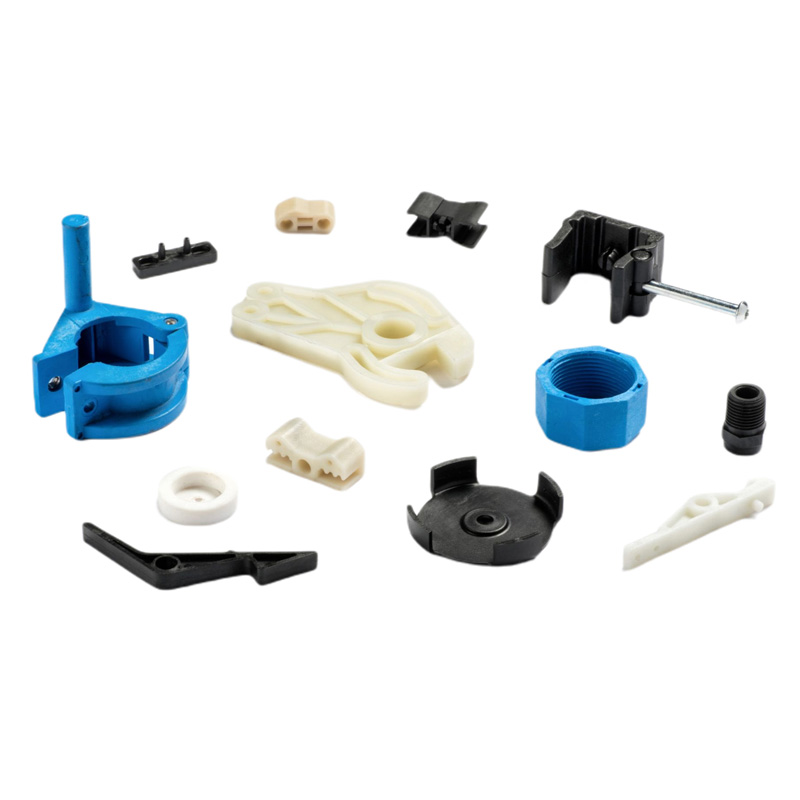
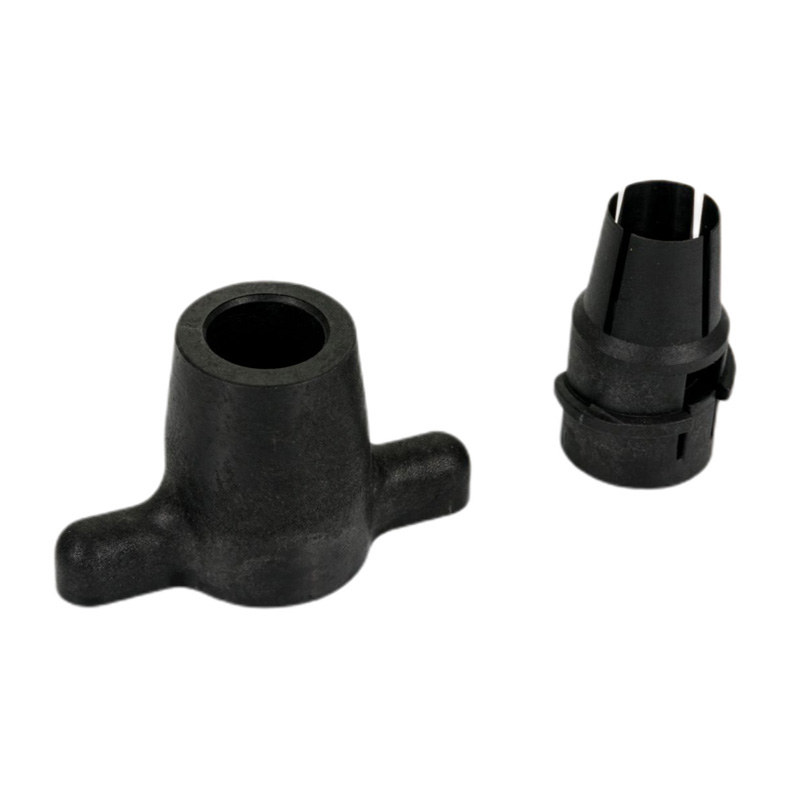
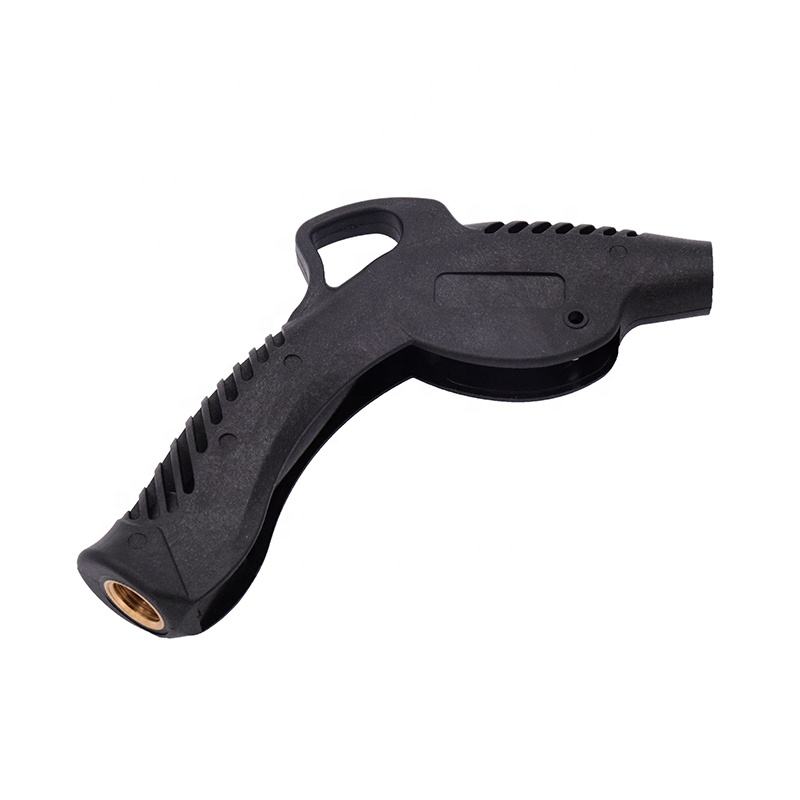
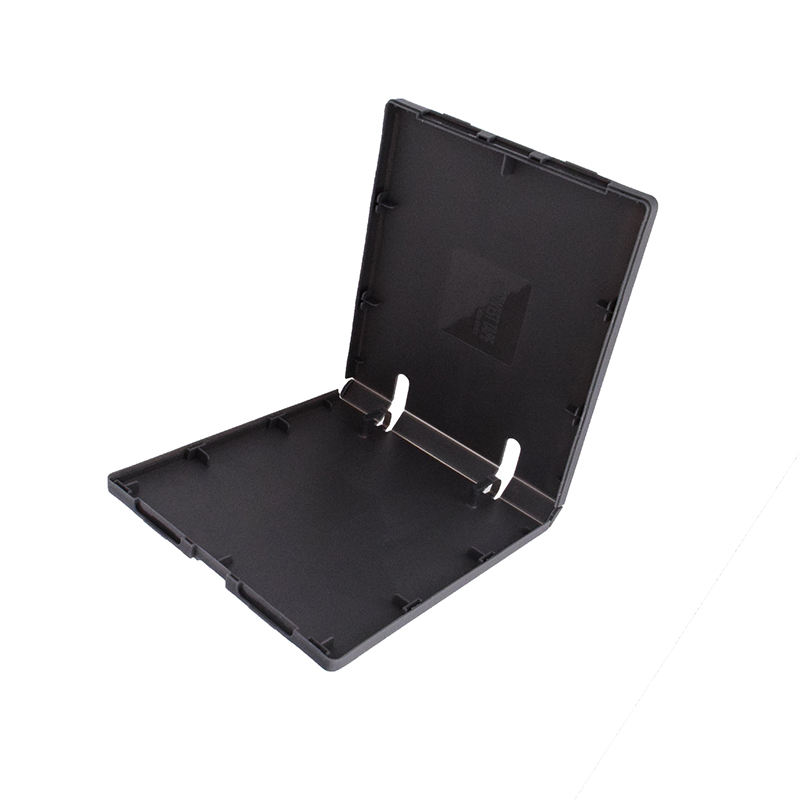
Injection Molding Plastic Parts
Youlin® Injection molding plastic parts are widely used today for both consumer products and engineering applications. Almost every plastic item around you was manufactured using injection molding. This is because the technology can produce identical parts at very high volumes at a very low cost per part.
Send Inquiry
1. What is Injection Molding Plastic Parts?
Injection molding is the most commonly used method for producing higher volumes of plastic parts.
Rapid Delivery of Youlin® Injection Molding Plastic Parts
Need low-volume parts quickly? Depending on your project requirements, our fast track injection molding can deliver parts in as little as ten days.
Experienced Injection Molding Project Management
Work directly with an experienced team, dedicated to delivering your parts in your timeline. By providing a mold-build schedule and regular project updates, you can depend on timely production with globally competitive pricing.
Injection Molding Production Capabilities
Access cutting-edge tooling manufacturing facilities, including high-speed CNC machines, EDM machines and press machine. These precise tooling operations complement our state-of-the-art injection molding capabilities.
Injection Molding Solutions Across Product Development
For new design verification utilizing our prototyping to production services in our state of the art facilities, we aim to provide end to end product development life cycle solutions. Injection molding is an ideal alternative to 3D printing for parts at a better cost per piece and in materials not available in 3D printing.
2. How to Make Injection Molding Plastic Parts

Here is the process of Youlin® injection molding plastic parts works:
1. The polymer granules are first dried and placed in the hopper, where they are mixed with the coloring pigment or the other reinforcing additives.
2. The granules are fed into the barrel, where they are simultaneously heated, mixed and moved towards the mold by a variable pitch screw. The geometry of the screw and the barrel are optimized to help build up the pressure to the correct levels and melt the material.
3. The ram then moves forwards and the melted plastic is injected into the mold through the runner system, where it fills the whole cavity. As the material cools down, it re-solidifies and takes the shape of the mold.
4. Finally, the mold opens and the now solid part is pushed out by the ejector pins. The mold then closes and the process repeats.
5.
The whole process can be repeated very fast: the cycle takes approximately 30 to 90 seconds depending on the size of the part.
After the part is ejected, it is dispensed on a conveyor belt or in a holding container. Usually, injection molded parts are ready to use right away and require little to no post-processing.
3. Advantages of Youlin Injection Molding Plastic Parts
✔ Production Grade Tooling: Production-grade steel tooling with T1 samples delivered within a week. Once your mold is created, we will send ten part samples (T1) for approval.
✔ Broad Material Selection: Choose from dozens of materials including ABS, Ultem, PC/ABS, PEEK, HDPE, PET, TPE, PET, nylon, polyethylene, and more
✔ Precision: Industry-leading delivery on tight tolerance projects
✔ Scalability: Mold prototypes or production runs of millions of parts
✔ Wide Range of Machines: Single, multi-cavity, and family molds; 50 to 1,100+ press tonnage; side actions including hand-loaded cores available
4. Common Materials Lists for Injection Molding Plastic Parts
|
Material |
Description |
Benefits |
Applications |
|
ABS |
Common thermoplastic with good impact resistance and toughness. |
● Good impact resistance with toughness and rigidity |
● Computer housings |
|
Polypropylene |
Thermoplastic polymer used for a wide number of applications. |
● Excellent moisture resistance |
● Packaging |
|
Polyoxymethylene (POM) |
Dimensionally stable thermoplastic with high stiffness and low friction. |
● High tensile strength with rigidity and toughness |
● Mechanical automotive |
|
Polycarbonate |
Thermoplastic material with good temperature resistance and impact strength. |
● High impact resistance |
● Automotive headlights |
|
Polycarbonate / ABS |
Blend of PC and ABS that creates strong parts for a variety of applications. |
● Good impact resistance with toughness ● and rigidity |
● Automotive exterior and interior components |
|
PVC |
PVC is a polymer with good insulation properties, high hardness, and good mechanical properties. |
● Wide range of flexibility |
● Medical/healthcare products |
|
Nylon |
Polymer material that is durable with high elongation and good abrasion resistance. |
● Temperature capability 600°-700° for short term |
● Automotive components |
|
Nylon 32% Glass Fiber |
Polymer with excellent mechanical stiffness and elevated temperature resistance. |
- |
- |
|
Acrylic (PMMA) |
Material with resistance to breakage often used for transparent applications. |
● Excellent optical clarity |
● Automotive transparent items such as head/tail lenses and trim |
|
Polystyrene |
Light weight material popular for its high impact strength and toughness. |
● Optical clarity |
● Household goods |
|
Polyetherimide (PEI) |
Thermoplastic with high heat resistance and excellent mechanical properties. |
● High heat resistance |
● Commercial aircraft interiors |
5. FAQ
Q: What are the 3 main parts of an injection molding machine?
A: An injection molding machine consists of 3 main parts: the injection unit, the mold - the heart of the whole process - and the clamping/ejector unit. In this section, we examine the purpose of each of these systems and how their basic operation mechanics affect the end-result of the Injection molding process.
Q: How do you identify common injection molding plastic parts defects?
A: Short Shots: Short shots are parts where the plastic did not completely fill out the cavity.
Sink Marks: Sink marks are depressions on the surface of the part. They usually occur in the thicker sections of the part.
Flash: Flash is a thin layer of plastic that flows beyond the parting line of the mold.
Q: What is core and cavity in injection molding?
A: The core is the male part which forms the internal shape of molding. The cavity is the female part which forms external shape of molding.